315-30-0
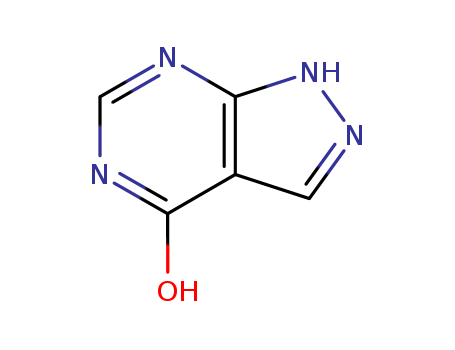
- Product Name:Allopurinol
- Molecular Formula:C5H4N4O
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:136.113
Product Details;
CasNo: 315-30-0
Molecular Formula: C5H4N4O
Appearance: white to off-white solid
Reputable Factory Supply 315-30-0 with Lowest Price, Buy Reliable Quality Allopurinol
- Molecular Formula:C5H4N4O
- Molecular Weight:136.113
- Appearance/Colour:white to off-white solid
- Vapor Pressure:0mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:>300 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.816
- Boiling Point:423.27 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:10.2(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:209.787 °C
- PSA:74.43000
- Density:1.702 g/cm3
- LogP:-0.35380
Allopurinol(Cas 315-30-0) Usage
|
Chemical Properties |
White to Off-White Solid Odorless tasteless white microcrystalline powder. |
|
Uses |
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor; decreases uric acid production. Used in treatment of hyperuricemia and chronic gout. Antiurolithic Allopurinol is utilized to prevent or reduce high uric acid levels in the blood, which can lead to conditions like gout or gouty arthritis. It is also employed to manage excess uric acid levels caused by cancer medications or in patients with kidney stones. Allopurinol functions by replacing purine in the body's purine metabolism pathway, thereby reducing the synthesis and accumulation of uric acid. Allopurinol is especially indicated in the treatment of chronic tophaceous gout, since patients receiving it show a pronounced decrease in their serum and urinary uric acid levels. Because it does not depend on renal mechanisms for its efficacy, allopurinol is particularly beneficial for patients who already have developed renal uric acid stones, patients with excessively high urate excretion (e.g., above 1,200 mg in 24 hours), patients with a variety of blood disorders (e.g., leukemia, polycythemia vera), patients with excessive tophus deposition, and patients who fail to respond well to the uricosuric drugs. Allopurinol also inhibits reperfusion injury. This injury occurs when organs that either have been transplanted or have had their usual blood perfusion blocked are reperfused with blood or an appropriate buffer solution. The cause of this injury is local formation of free radicals, such as the superoxide anion, the hydroxyl free radical, or peroxynitrite. These substances are strong oxidants and are quite damaging to tissues. |
|
Indications |
Allopurinol (Zyloprim) is the drug of choice in the treatment of chronic tophaceous gout and is especially useful in patients whose treatment is complicated by renal insufficiency. |
|
Brand name |
Lopurin (Abbott); Lopurin (BASF); Zyloprim (Promethus). |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor, Gout therapy |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Allopurinol are not available; however, Allopurinol is probably combustible. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Inhibitor of xanthine oxidase and de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. A classical agent in treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. |
|
Pharmacokinetics |
Allopurinol was synthesized in 1956 as part of a study of purine antagonists. It is well absorbed on oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations appearing within 1 hour. Decreases of uric acid can be observed within 24 to 48 hours. Excretion of allopurinol and its metabolite occurs primarily in the urine, with approximately 20% of a dose being excreted in the feces. |
|
Side effects |
Common toxicities associated with allopurinol administration include a variety of skin rashes, gastrointestinal upset, hepatotoxicity, and fever. These reactions are often sufficiently severe to dictate termination of drug therapy. It is advised that therapy not be initiated during an acute attack of gouty arthritis. As with the uricosuric drugs, therapy with allopurinol should be accompanied both by a sufficient increase in fluid intake to ensure water diuresis and by alkalinization of the urine. Prophylactic use of colchicine also helps to prevent acute attacks of gout that may be brought on during the initial period of allopurinol ingestion. |
|
Safety Profile |
Human poison by ingestion. Poison experimentally by intraperitoneal and subcutaneous routes. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects by ingestion: blood leukopenia, dermatitis, jaundice, muscle weakness, thrombocytopenia. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. An FDA proprietary drug used as a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H4N4O/c10-5-3-1-8-9-4(3)6-2-7-5/h1-2H,(H2,6,7,8,9,10)
315-30-0 Relevant articles
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Allopurinol
G. A. C. Murrell & W. G. Rapeport
, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Volume 11, pages 343–353, (1986)
In animals, allopurinol is found in highest concentrations in vascular tissue, blood, liver, intestine and heart. It is negligibly bound to plasma proteins. Oxypurinol is eliminated by the kidney and has a much longer elimination half-life than allopurinol. Oxypurinol accumulates in patients with renal dysfunction; hence allopurinol dosages should be adjusted in such patients. Allopurinol inhibits the metabolism of 6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine, which require dosage modifications. The interaction of allopurinol with oral anticoagulants and phenytoin has not been clearly established in clinical practice.
Synthetic method of 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4-ol
-
Paragraph 0024; 0027-0028; 0033; 0036; 0039; 0042, (2018/11/27)
The invention discloses a synthetic meth...
Synthetic method of allopurinol
-
Paragraph 0005; 0028-0029; 0032-0033; 0036-0037; 0040-0041, (2018/03/01)
The invention relates to a synthetic met...
Efficient synthesis of14C-labeled 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine and related [4.3.0]-bicyclic pyrimidino systems
Ho, Jonathan Z.,Van Arsdale, Kyle R.,Braun, Matthew P.
scheme or table, p. 958 - 963 (2009/03/11)
In support of a research program aimed a...
INHIBITORS OF Akt ACTIVITY
-
Page/Page column 181, (2010/11/27)
Invented are novel thiophene compounds, ...
315-30-0 Upstream products
-
6994-25-8
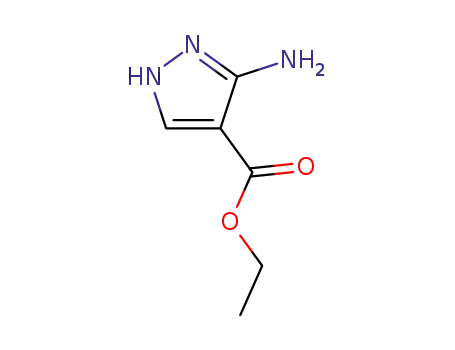
3-amino-4-pyrazolecarboxylic acid ethyl ester
-
77287-34-4
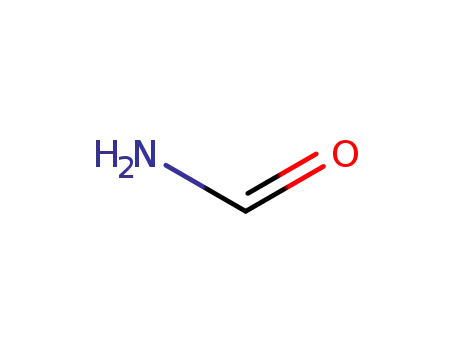
formamide
-
27511-79-1
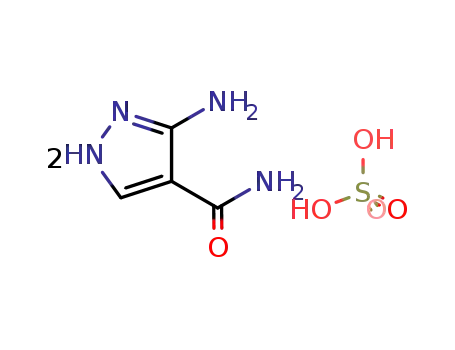
3-amino-4-pyrazolocarboxamide hemisulfate
-
52739-52-3
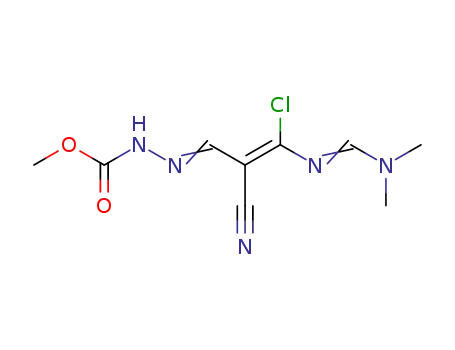
2-Methoxycarbonylhydrazonomethyl-3-chlor-5-dimethylamino-4-aza-2,4-pentadiennitril
315-30-0 Downstream products
-
57121-50-3
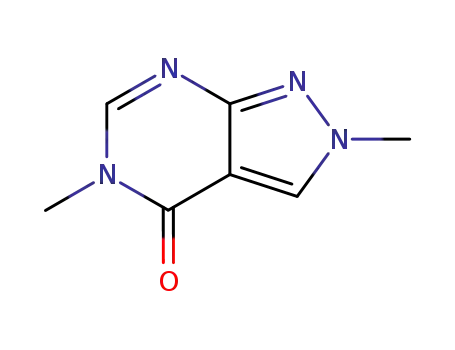
2,5-dihydro-2,5-dimethyl-4H-pyrazolo<3,4-d>pyrimidin-4-one
-
5334-54-3
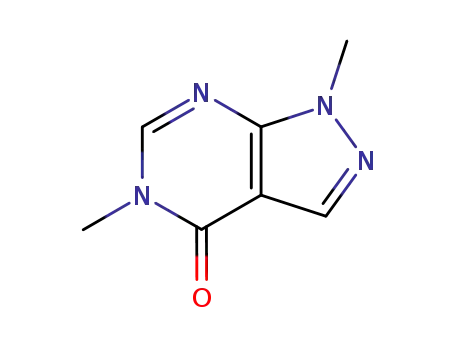
1,5-dimethylallopurinol
-
5334-23-6
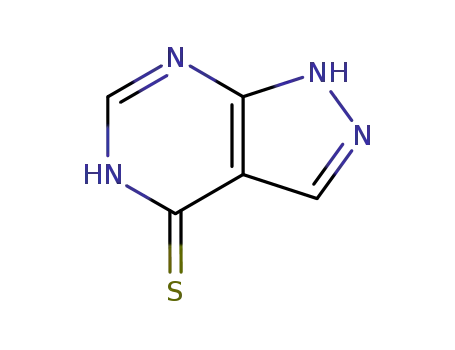
4-Mercapto-1H-pyrazolo<3,4-d>pyrimidine
-
5399-92-8
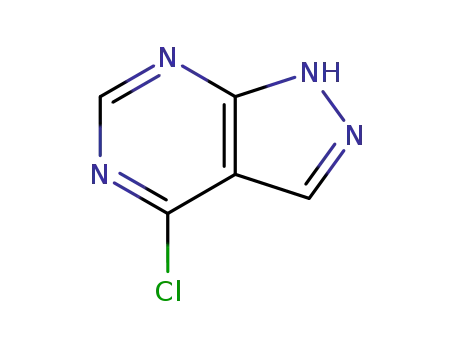
4-chloro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine
Relevant Products
-
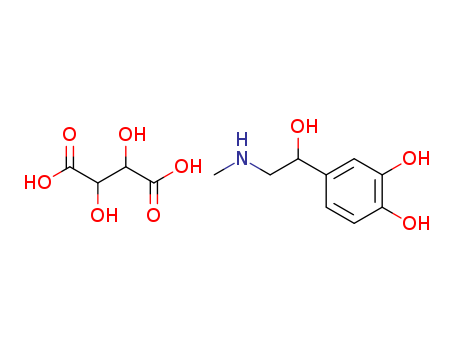
Epinephrine bitartrate
CAS:51-42-3
-
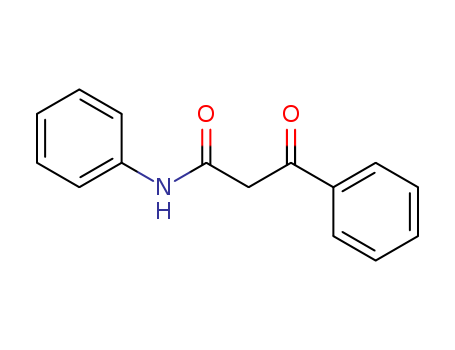
2-BENZOYLACETANILIDE
CAS:959-66-0
-
Salicylamide
CAS:65-45-2