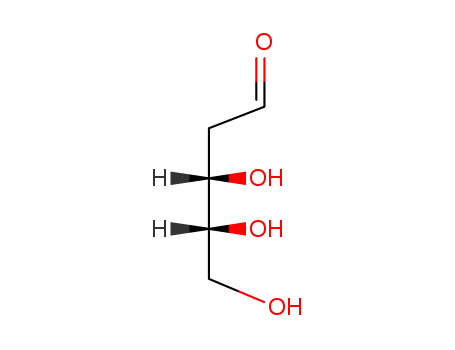
533-67-5
- Product Name:2-Deoxy-D-ribose
- Molecular Formula:C5H10O4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:134.132
Product Details;
CasNo: 533-67-5
Molecular Formula: C5H10O4
Appearance: white to off-white crystalline powder
Chinese Factory Supply 2-Deoxy-D-ribose 99% Pure 533-67-5 with Fast Delivery
- Molecular Formula:C5H10O4
- Molecular Weight:134.132
- Appearance/Colour:white to off-white crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:0mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:89-90 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:-56 ° (C=1, H2O)
- Boiling Point:379.684 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:12.61(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:197.601 °C
- PSA:69.92000
- Density:1.516 g/cm3
- LogP:-1.55310
2-Deoxy-D-ribose(Cas 533-67-5) Usage
|
Description |
2-deoxy-D-Ribose is a reducing sugar formed as a degradation product during metabolism of thymidine by thymidine phosphorylase. It increases levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in HL-60 human leukemia cells when used at a concentration of 15 mM. 2-deoxy-D-Ribose (10 μM) induces tubulogenesis and migration of bovine aortic endothelial (BAE) cells. Topical administration of 2-deoxy-D-ribose increases blood vessel formation and accelerates wound healing in a rat full-thickness cutaneous wound model. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White powder |
|
Uses |
2-deoxy-D-ribose is a deoxypentose that is D-ribose in which the hydroxy group at position C-2 is replaced by hydrogen. It is used as a precursor to deoxyribonucleic acid. It induces apoptosis by inhibiting the synthesis and increasing the efflux of glutathione. Further, it is used in the synthesis of optically active dipyrrolyl alkanols from pyrroles on the surface of montmorillonite KSF clay. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: 2-deoxy-D-ribose is a deoxypentose that is D-ribose in which the hydroxy group at position C-2 is replaced by hydrogen. It has a role as a human metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is functionally related to a D-ribose. |
|
Purification Methods |
Dissolve 2-deoxy--D-ribose in a little H2O, evaporate to a syrup (in a vacuum), and seed to crystallise. Triturate the crystals with a little EtOAc containing 5% MeOH, decant and dry in vacuum over P2O5. It is best purified via the anilide which separates from a mixture of the ribose (100-125g) in MeOH (100mL) and redistilled aniline (40mL) in a few minutes. After standing for 20hours at room temperature, it is cooled to 0o, filtered, washed with 50% aqueous MeOH and Et2O followed by recrystallisation from ethylene glycol monomethyl ether. The anilide has m 172-173o, [ ] D 25 +46o (equilibrium in pyridine). The anilide (5g), benzaldehyde (5mL) and benzoic acid (0.5g) in H2O (150mL) are shaken mechanically for 2024hours. The aqueous phase is extracted with Et2O (3x), decolourised with a little charcoal and evaporated in a vacuum to a syrup. This is dried over P2O5 in high vacuum. The syrupy sugar weighs 3.1g and crystallises in a few days, but more rapidly on seeding. Triturate it with a little EtOAc containing 5% MeOH, decant and dry it over P2O5. At this stage it has m 78-82o, [ ] D 25 -57o (c 1, H2O final). This is a mixture of and anomers. Pure -anomer is obtained by recrystallisation from EtOAc The -anomer when recrystallised from EtOAc and isoPrOH has m 96-98o, [ ] D 25 -55o (c 0.5, H2O final). [Sowden Biochemical Preparations 5 75 1957.] The mutarotation is as follows: [] D 20.5 +96.3o(0minutes), -76o(33minutes), -56o (24hours) (c 5.8 MeOH). It is moderately hygroscopic and should be kept in a well stoppered bottle. It also crystallises from diethyl ether. [Deriaz et al. J Chem Soc 1879 1949, Beilstein 1 IV 4181, Hauske & Rapoport J Org Chem 4 4 2472 1979.] |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H10O4/c6-2-4-3(7)1-5(8)9-4/h3-8H,1-2H2/t3-,4+,5-/m0/s1
533-67-5 Relevant articles
Conversion of 2,3-O-isopropylidene-D-glyceraldehyde into 2-deoxy-D-erythro-pentose
Hoffmann, Reinhard W.,Endesfelder, Andreas,Zeiss, Hans-J.
, p. 320 - 325 (1983)
-
Prebiotic synthesis of 2-deoxy-d-ribose from interstellar building blocks promoted by amino esters or amino nitriles
Steer, Andrew M.,Bia, Nicolas,Smith, David K.,Clarke, Paul A.
supporting information, p. 10362 - 10365 (2017/09/25)
Understanding the prebiotic genesis of 2...
Thymidine phosphorylase, 2-deoxy-D-ribose and angiogenesis
NS BROWN, R BICKNELL
, Biochemical Journal, 1998
In contrast, 2-deoxy-d-ribose appears to lack a cell-surface receptor. Glucose is another sugar that acts as an endothelial-cell chemoattractant. The migratory activity of glucose is blocked by ouabain. It is possible that 2-deoxy-d-ribose and glucose stimulate endothelial-cell migration via a similar mechanistic pathway.
Molecular Basis for the Inhibition of Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis by 2-Deoxy-d-ribose
Ryuji Ikeda, Tatsuhiko Furukawa, Masaki Kitazono, Kenji Ishitsuka, Hiroshi Okumura, Ayako Tani, Tomoyuki Sumizawa, Misako Haraguchi, Masaharu Komatsu, Hiroshi Uchimiya, Xiao-Qin Ren, Toshiro Motoya, Katsushi Yamada, Shin-ichi Akiyama 1
, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications Volume 291, Issue 4, 8 March 2002, Pages 806-812
2-Deoxy-d-ribose, a degradation product of thymidine generated by TP enzymatic activity partially prevented hypoxia-induced apoptosis. 2-Deoxy-d-ribose inhibits a number of components of the caspase-mediated hypoxia-induced apoptotic pathway.
The 1H NMR method for the determination of the absolute configuration of 1,2,3-prim,sec,sec-triols
Lallana, Enrique,Freire, Felix,Seco, Jose Manuel,Quinoa, Emilio,Riguera, Ricardo
, p. 4449 - 4452 (2007/10/03)
The absolute configuration of 1,2,3-prim...
533-67-5 Process route
-
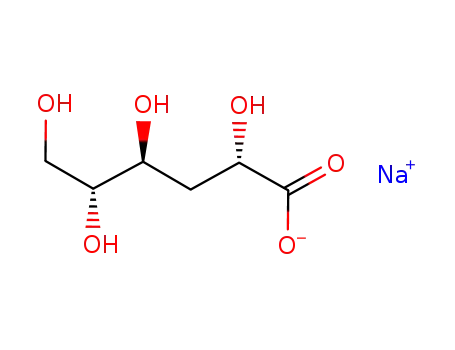
- 93857-40-0
sodium 3-deoxy-D-mannonate

-
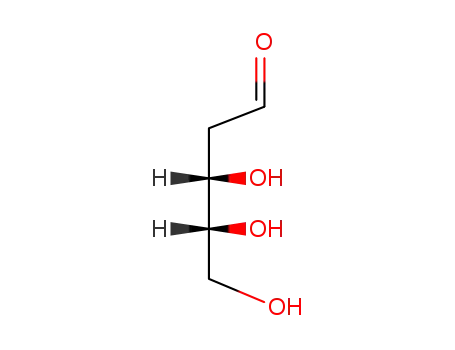
- 533-67-5
2-Deoxy-D-ribose
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
sodium 3-deoxy-D-mannonate; With hydrogenchloride; In water; pH=5;
With sodium hypochlorite; acetic acid; In water; at 40 - 45 ℃; for 2h; pH=5 - 6;
|
95% |
|
sodium 3-deoxy-D-mannonate; With hydrogenchloride; In water; pH=5;
With hydrogenchloride; sodium hypochlorite; acetaldehyde; In water; at 40 - 45 ℃; for 2h; pH=5 - 6;
|
94% |
|
sodium 3-deoxy-D-mannonate; With hydrogenchloride; In water; pH=5;
With hydrogenchloride; sodium hypochlorite; formaldehyd; In water; at 40 - 45 ℃; for 2h; pH=5 - 6;
|
94% |
|
sodium 3-deoxy-D-mannonate; With hydrogenchloride; In water; pH=5;
With sodium hypochlorite; acetaldehyde; acetic acid; In water; at 40 - 45 ℃; for 2h; pH=5 - 6;
|
94% |
|
sodium 3-deoxy-D-mannonate; With sodium hypochlorite; In water; for 1 - 4h; pH=4.5 - 5.0;
With sodium sulfite; In water;
|
93% |
|
sodium 3-deoxy-D-mannonate; With hydrogenchloride; In water; pH=5;
With sodium hypochlorite; formic acid; In water; at 40 - 45 ℃; for 2h; pH=5 - 6;
|
93% |
-
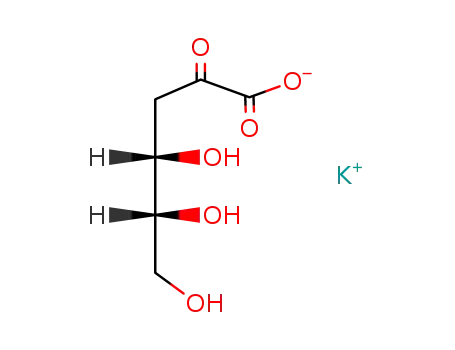
-
potassium 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate

-

- 533-67-5
2-Deoxy-D-ribose
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
potassium 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate; With sulfuric acid; hydrogen; palladium 10% on activated carbon; In water; at 50 ℃;
With calcium carbonate; In water;
With calcium hydroxide; carbon dioxide; dihydrogen peroxide; copper diacetate; iron(II) sulfate; more than 3 stages;
|
47% |
533-67-5 Upstream products
-
2490-91-7
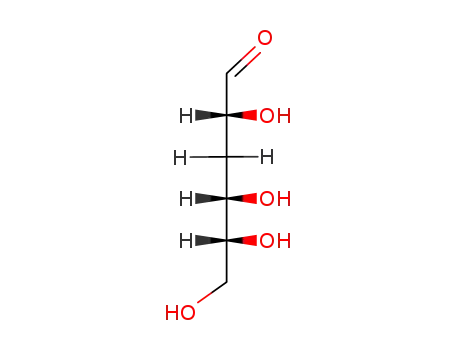
3-deoxy-D-glucose
-
50-99-7
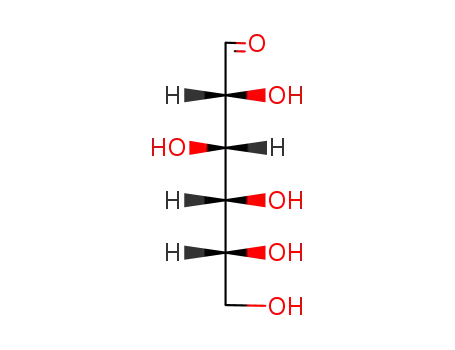
D-glucose
-
146-72-5
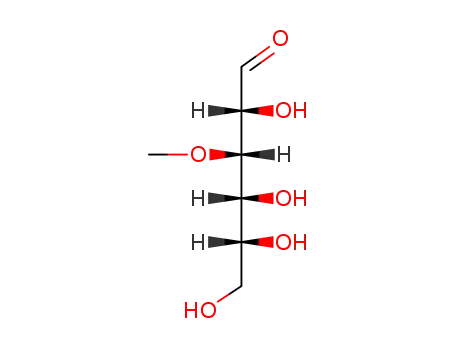
3-O-methyl-D-glucose
-
50705-39-0
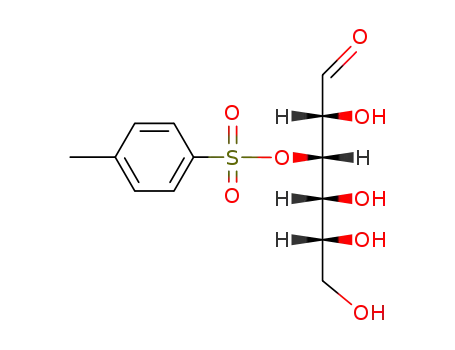
O3-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)-D-glucose
533-67-5 Downstream products
-
7284-15-3
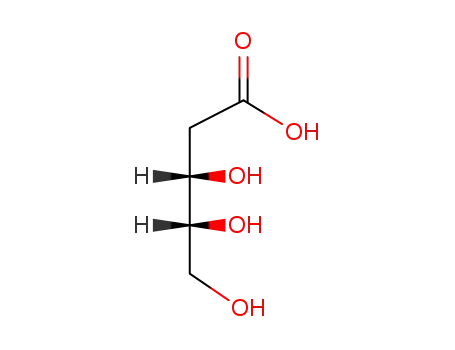
2-deoxy-D-ribonic acid
-
51255-17-5
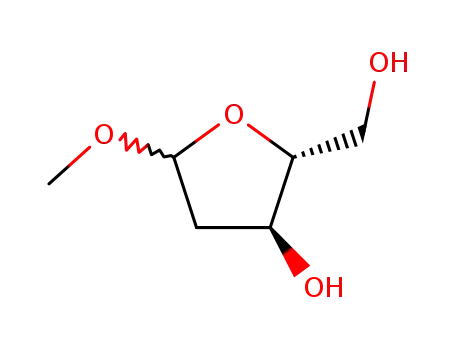
1-O-methyl-2-deoxy-D-ribofuranoside
-
17685-02-8
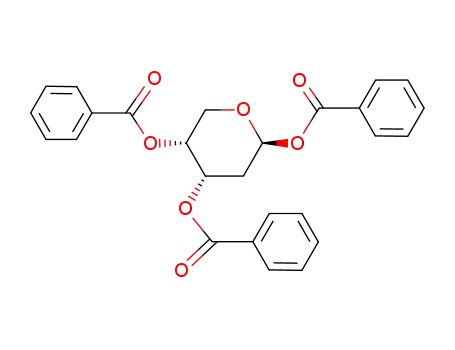
1,3,5-tri-O-benzoyl-2-deoxy-β-D-ribopyranosa
-
17685-01-7
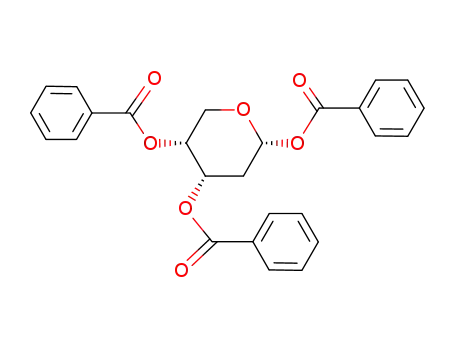
tri-O-benzoyl-α-D-erythro-2-deoxy-pentopyranose
Relevant Products
-
Epinephrine bitartrate
CAS:51-42-3
-
Propranolol Hydrochloride
CAS:3506-09-0
-
Rimantadine hydrochloride
CAS:1501-84-4