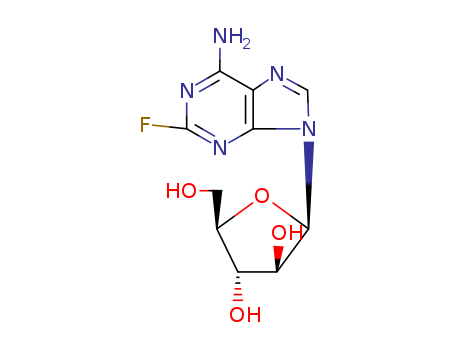
21679-14-1
- Product Name:Fludarabine
- Molecular Formula:C10H12FN5O4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:285.235
Product Details;
CasNo: 21679-14-1
Molecular Formula: C10H12FN5O4
Appearance: white solid
Buy High Grade Reputable Factory Supply Fludarabine 21679-14-1 On Stock
- Molecular Formula:C10H12FN5O4
- Molecular Weight:285.235
- Appearance/Colour:white solid
- Vapor Pressure:1.86E-23mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:265-268 °C
- Refractive Index:1.876
- Boiling Point:747.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:13.05±0.70(Predicted)
- Flash Point:405.8 °C
- PSA:139.54000
- Density:2.17 g/cm3
- LogP:-1.25970
Fludarabine(Cas 21679-14-1) Usage
|
Description |
Fludarabine (21679-14-1) is a synthetic adenosine analog that inhibits DNA biosynthesis and is a clinically useful antineoplastic agent.1 In cells fludarabine accumulates as its 5’-triphosphate (F-ara-ATP) for which the rate-limiting step in formation is the conversion of fludarabine to its monophosphate.2 F-ara-ATP has multiple mechanisms of action including inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase, DNA polymerase, ligase and primase.2 A frequently used agent in myeloablative conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.3 Immunosuppressive effects are mediated via inhibition of TNFa-stimulated production of IL-2 and IFN-g through inactivation of NFkB.4 Antagonist at adenosine A1 receptors.5 |
|
Chemical Properties |
White Solid |
|
Originator |
Fludarabine,Union Pharmaceutical |
|
Uses |
Fludarabine is not one of the most used drugs in pediatric oncology area. It is used in combination with other drugs to treat AML in children, mostly those who are receiving second-line therapy. It is commonly sold as 10 mg film-coated tablets and IV vial containing 50mg. |
|
Indications |
Fludarabine (Fludara) is a fluorinated purine analogue of the antiviral agent vidarabine.The active metabolite, 2-fluoro-ara-adenosine triphosphate, inhibits various enzymes involved in DNA synthesis, including DNA polymerase-α, ribonucleotide reductase, and DNA primase. Unlike most antimetabolites, it is toxic to nonproliferating as well as dividing cells, primarily lymphocytes and lymphoid cancer cells. The drug is highly active in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, with approximately 40% of patients achieving remissions after previous therapy with alkylating agents has failed. Activity is also seen in the low-grade lymphomas. The major side effect is myelosuppression, which contributes to fevers and infections in as many as half of treated patients. Nausea and vomiting are mild. Occasional neurotoxicity has been noted at higher doses, with agitation, confusion, and visual disturbances. |
|
Preparation |
Synthesis of fludarabine 1: 2-Fluoroadenine is reacted with 9-β-D-arabinosyl-uracile, taking water as a solvent. The reaction will take place in the presence of Enterobacter aerogenes. Fludarabine so formed is then treated with acetic anhydride to form the acetylderivative.The acetyl derivative is then crystallize to get back the pure Fludarabine.Synthesis of fludarabine 2: 2,4,5,6-tetraaminopyrimidine and formamide were cyclized together by heating to give 2,6-diaminopurine. acylation with acetic anhydride-pyridine complex gave 2,6-diacetamidopurine. then reacted with 2,3,5-tri-o-benzyl-d-arabinofuranosyl chloride to give compound (i). (i) was deacetylated to give compound (ii). (ii) in fluoroboronic acid-tetrahydrofuran, first nitrosated and then substituted to give compound (ili). in the presence of boron trichloride, the benzyl group was removed to give fludarabine. the yield was 17.5% in terms of 2,3,5-tri-o-benzyl-d-arabinofuranosyl chloride. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antineoplastic |
|
General Description |
The drug is available as the phosphate salt in a 50-mg vialfor IV use. Fludarabine is used to treat chronic lymphocyticleukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The mechanism ofaction involves the triphosphate metabolite and its inhibitionof DNA chain elongation. The 2-fluoro group on the adeninering renders fludarabine resistant to breakdown byadenosine deaminase. The drug is rapidly dephosphorylatedto 2-fluoro-ara-adenosine (F-ara-A) after administration. Fara-A is taken into the cell and subsequently re-phosphorylatedto yield the triphosphate (F-ara-ATP), the active drugspecies. Resistance can occur via decreased expression ofthe activating enzymes and decreased drug transport.Fludarabine is orally bioavailable and is distributed throughoutthe body reaching high levels in liver, kidney, andspleen. The drug is metabolized to F-ara-A, which enterscells via the nucleoside transport system and is rephosphorylatedby deoxycytidine kinase to fludarabine monophosphateand finally fludarabine triphosphate, the activespecies. About 25% of F-ara-A is excreted unchanged inurine. Drug interactions include an increased incidence offatal pulmonary toxicity when fludarabine is used in combinationwith pentostatin. Additionally, fludarabine may potentiate the effects of several other anticancer drugs includingcytarabine, cyclophosphamide, and cisplatin.Toxicities include myelosuppression, immunosuppression,fever, nausea, and vomiting. |
|
Biological Activity |
Purine analog that inhibits DNA synthesis. Exhibits antiproliferative activity (IC 50 = 1.54 μ M in RPMI cells) and triggers apoptosis through increasing Bax and decreasing Bid, XIAP and survivin expression. Displays anticancer activity against hematological malignancies in vivo . |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Fludarabine (the 5′-phosphate) is a prodrug that is converted to F-ara-A, which enters cells and accumulates primarily as the 5′-triphosphate. F-ara-A interferes with DNA synthesis and repair and induces apoptosis of cancer cells. F-ara-A also strongly inhibits DNA methylation, particularly methylation of cytosine in CpG dinucleotide sequences. |
|
Mode of action |
Fludarabine is a fluorinated analogue of adenine that is relatively resistant to deamination by adenosine deaminase. Fludarabine phosphate is a prodrug that is rapidly dephosphorylated to 2-fluoro-ara-A and then phosphorylated intracellularly by deoxycytidine kinase to the active metabolite triphosphate 2-fluoro-ara-ATP. Fludarabine inhibits the DNA synthesis via inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase, DNA polymerase (α, δ, and ε), DNA primase, and DNA ligase. The action mechanism also is by partial inhibition of RNA polymerase II, causing reduction in protein synthesis. It is believed that effects on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis contribute to the inhibition of cell growth, mostly by inhibition of DNA synthesis. Lymphocytes of CLL when exposed, in vitro, to the compound 2-fluoro-ara-A lead to extensive DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. |
InChI:InChI=1/C10H12FN5O4/c11-10-14-7(12)4-8(15-10)16(2-13-4)9-6(19)5(18)3(1-17)20-9/h2-3,5-6,9,17-19H,1H2,(H2,12,14,15)/t3-,5-,6+,9-/m1/s1
21679-14-1 Relevant articles
Practical Synthesis of Fludarabine and Nelarabine
Bai, Jiang,Ding, Haixin,Liu, Jiang,Ouyang, Wenliang,Shen, Chunyang,Xiao, Qiang
, p. 417 - 423 (2020/01/23)
A new practical synthesis strategy has b...
Synthesis method of fludarabine phosphate
-
Paragraph 0041-0043; 0056-0060, (2020/08/22)
The invention provides a synthesis metho...
Synthesis method of fludarabine and nelarabine
-
Paragraph 0054-0060, (2020/01/11)
The present invention discloses a synthe...
Enzymatic Synthesis of Therapeutic Nucleosides using a Highly Versatile Purine Nucleoside 2’-DeoxyribosylTransferase from Trypanosoma brucei
Pérez, Elena,Sánchez-Murcia, Pedro A.,Jordaan, Justin,Blanco, María Dolores,Manche?o, José Miguel,Gago, Federico,Fernández-Lucas, Jesús
, p. 4406 - 4416 (2018/09/14)
The use of enzymes for the synthesis of ...
21679-14-1 Process route
-
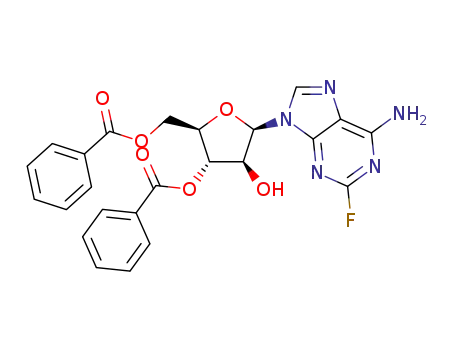
-
2-fluoro-9-(3,5-di-O-benzoyl-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)adenine

-
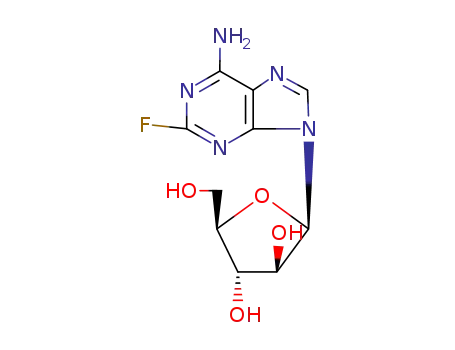
-
146-78-1,19768-92-4,21679-14-1,21679-15-2
Fludarabine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
methanol; ammonia;
at 0 - 40 ℃;
for 6h;
Autoclave;
|
93% |
|
With
ammonia;
In
methanol;
at 40 ℃;
for 6h;
|
90% |
-
-
C45H32FN5O9

-

-
146-78-1,19768-92-4,21679-14-1,21679-15-2
Fludarabine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
ammonium hydroxide; acetic acid;
In
methanol;
at 20 ℃;
|
86.4% |
21679-14-1 Upstream products
-
75607-67-9
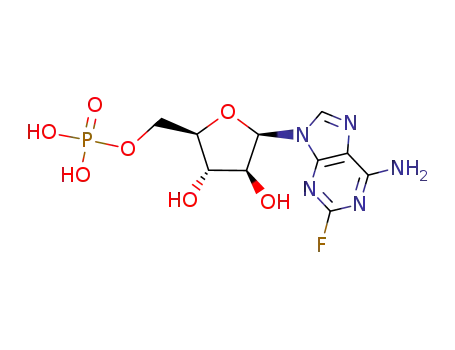
fludarabine phosphate
-
52522-49-3
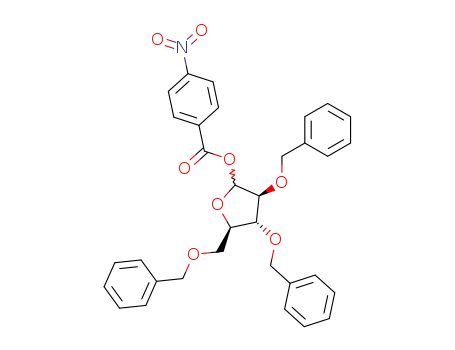
2,3,5-tri-O-benzyl-1-(4-nitrobenzoyloxy)-D-arabinofuranose
-
4060-34-8
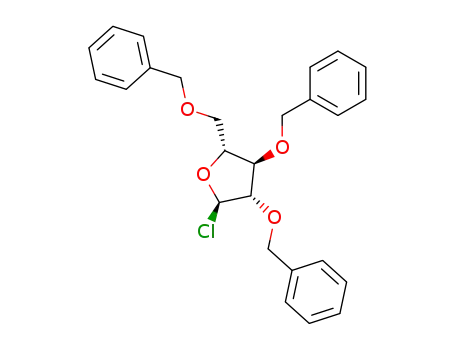
2,3,5-tri-O-benzyl-α-D-arabinofuranosyl chloride
-
143482-58-0
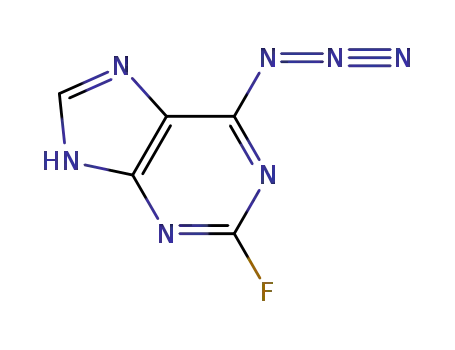
6-azido-2-fluoropurine
21679-14-1 Downstream products
-
700-49-2
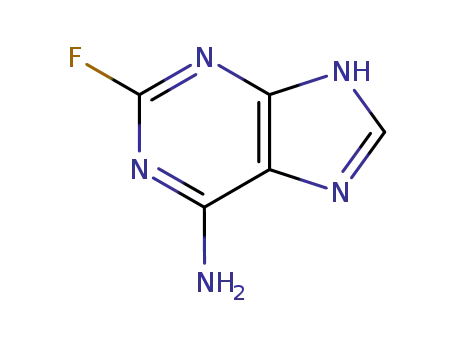
2-fluoroadenine
-
72075-46-8
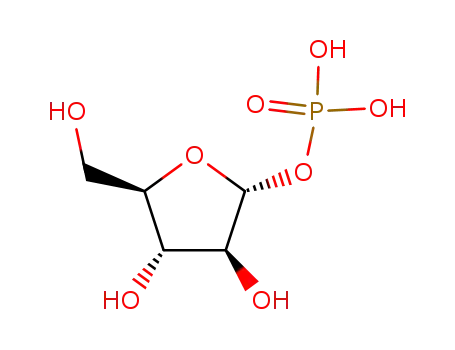
O1-Phosphono-α-D-arabinofuranose
-
75607-67-9

fludarabine phosphate
Relevant Products
-
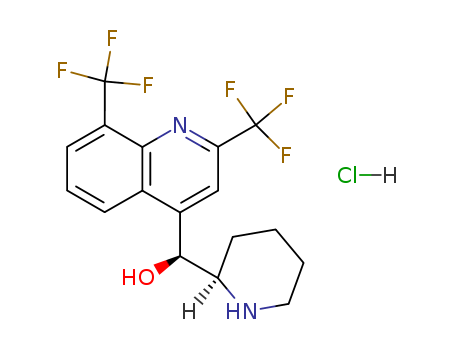
Mefloquine hydrochloride
CAS:51773-92-3
-
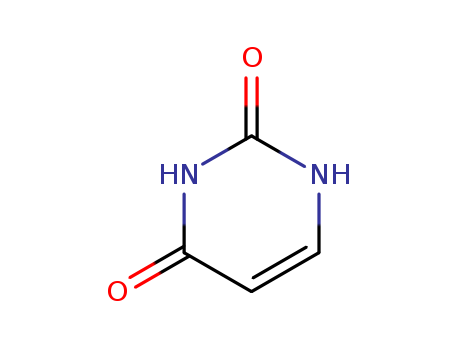
Uracil
CAS:66-22-8
-
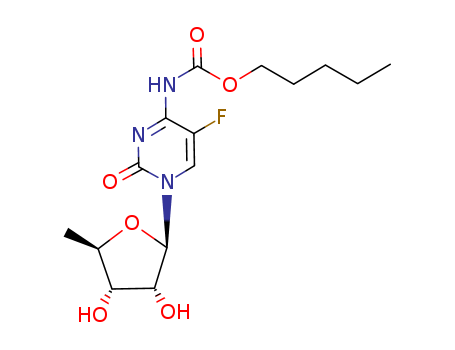
Capecitabine
CAS:158798-73-3