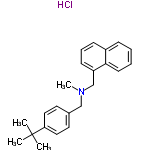
101827-46-7
- Product Name:N-SULPHAMYL-3-CHLOROPROPIONAMIDINE
- Molecular Formula:C23H27N.HCl
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:353.19
Product Details;
CasNo: 101827-46-7
Molecular Formula: C23H27N.HCl
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Top Purity 99% Factory Supply High Purity N-SULPHAMYL-3-CHLOROPROPIONAMIDINE 101827-46-7 with Fast Delivery
- Molecular Formula:C23H27N.HCl
- Molecular Weight:353.19
- Appearance/Colour:White crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:1.82E-07mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:210-214 °C
- Boiling Point:426.1 °C at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:187.7 °C
- PSA:3.24000
- Density:1.032 g/cm3
- LogP:6.57130
Butenafine hydrochloride(Cas 101827-46-7) Usage
|
Description |
Butenafine hydrochloride is a new benzylamine antifungal which appears to block the squalene epoxidation step of sterol synthesis in fungi. Active against a broad spectrum of fungi, butenafine hydrochloride is more effective in a guinea-pig model of tinea pedis than clotrimazole, naftifine and tolnaftate. Its efficacy is partially attributed to its long retention time in the skin. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White Solid |
|
Originator |
Kaken (Japan) |
|
Uses |
Butenafine HCl is a synthetic benzylamine antifungal, works by inhibiting the synthesis of sterols by inhibiting squalene epoxidase. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: The hydrochloride salt of butenafine. An inhibitor of squalene epoxidase, an enzyme responsible for the creation of sterols needed in fungal cell membranes, it is used for treatment of dermatological fungal infections. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
N-Methyl-1-naphtylmethylamine hydrochloride (2.1 g, 0.01 mole) was dissolved in 50 ml of dry dimethylformamide, and 3.71 g (0.035 mole) of anhydrous sodium carbonate was added, then 2.49 g (0.011 mole) of p-tbutylbenzyl bromide was added by stirring and the mixture was reacted at 30° to 40°C for 5 hours. Ice water was added, and the mixture was extracted with toluene. The organic layer was washed with water, and toluene was evaporated. The residue was chromatographed on silica gel column, and eluated with 5% ethyl acetate/n-hexane. The eluate was concentrated to give 2.98 g (yield 94%) of an oily substance. Hydrochloric acid/ethanol was added to 1 g of this oily product, and the mixture was concentrated. The residue was recrystallized from methanol/acetic acid to give 0.95 g of desired 1- naphthalenemethanamine, N-((4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl)methyl)-Nmethyl-, hydrochloride having melting point 200° to 202°C. |
|
Brand name |
Lotrimin (Schering); Mentax (Mylan Bertek);Volley. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antifungal |
|
General Description |
Butenafine hydrochloride is chemically known as N-4-tertbutylbenzyl-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethylamine hydrochloride. Butenafine, a benzylamine derivative, is a new generation antimycotic compound. It is easily soluble in methanol, ethanol, dichloromethane, and chloroform, but not in water. The allyl radical in butenafine hydrochloride is substituted by a butylbenzyl group. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Butenafine exhibits fungicidal and antimycotic activity. This fungal squalene epoxidase inhibitor serves as an effective fungicide against T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, Microsporum canis, Aspergillus fumigatus, Sporothrix schenckii, Candida parapsilosis, and C. albicans. It is considered more effective and rapid than other antifungal drugs at curing dermatophytosis and preventing recurrences. In humans, it is used topically to treat tinea conditions and superficial candidiasis. Butenafine is considered a promising antimycotic compound to treat tinea pedis due to its efficiency, safety profile, relapse rates, and cost-effectiveness. |
InChI:InChI=1/C23H27N.ClH/c1-23(2,3)21-14-12-18(13-15-21)16-24(4)17-20-10-7-9-19-8-5-6-11-22(19)20;/h5-15H,16-17H2,1-4H3;1H
Relevant Products
-
Benzathine Cloxacillin
CAS:23736-58-5
-
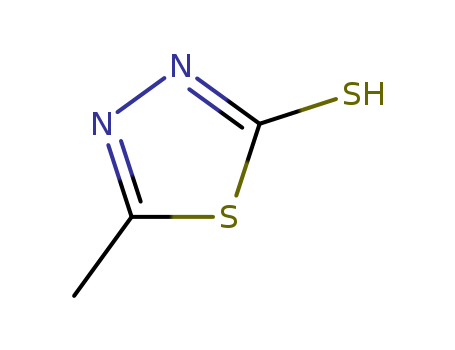
5-methyl-3H-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione
CAS:29490-19-5
-
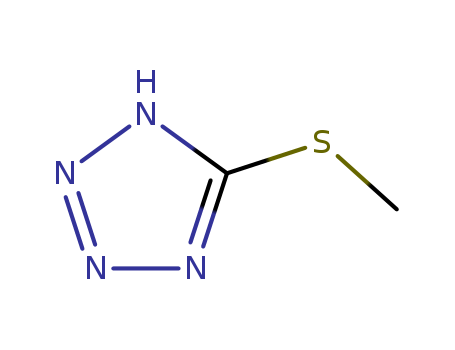
5-methylthiotetrazole
CAS:29515-99-9